What is Hybrid Energy system ?
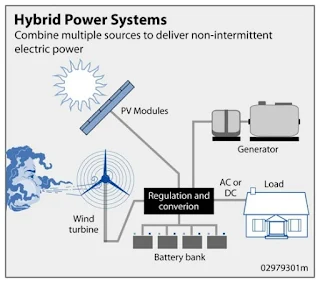
A hybrid energy system (HES) integrates multiple energy sources, typically combining renewable energy technologies like solar, wind, hydro, and biomass with conventional power generation methods to optimize energy efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. The key aim of HES is to reduce dependency on a single energy source, enhance energy security, and support decentralized power generation.
Hybrid Energy Systems: An Overview
Hybrid energy systems are designed to blend different energy generation methods to maximize output and efficiency. These systems can be grid-connected or off-grid, providing flexibility in power supply. The combination of renewable sources—solar, wind, hydro, and biomass—alongside conventional energy (e.g., diesel generators or natural gas) allows for a more resilient and reliable power supply, especially in regions with variable renewable energy availability.
The Need for Decentralization in India
India's ambitious renewable energy targets, particularly the goal of achieving 175 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2022 (100 GW from solar and 60 GW from wind), have underscored the importance of decentralized energy systems. Decentralization involves distributing energy generation closer to the point of use, reducing transmission losses, enhancing energy security, and providing power to remote and rural areas.
Decentralized systems, often referred to as Distributed Energy Resources (DERs), can include microgrids, rooftop solar, small-scale wind farms, and hybrid systems that combine different energy sources. The benefits of decentralization are manifold:
- Energy Access: Providing reliable power to off-grid areas.
- Reduced Transmission Losses: Energy is generated and consumed locally.
- Increased Energy Security: Reduces reliance on centralized grids that may be vulnerable to outages.
- Promotes Renewable Integration: Facilitates the integration of renewables into the grid by providing localized energy storage and generation.
Developments to Increase Decentralization in India
India is making strides in decentralizing its energy generation, driven by policy support, technological advancements, and the growing need for sustainable energy solutions. Some key developments include:
Microgrids and Mini-Grids: These small-scale, localized grids are designed to provide electricity to rural and remote areas. Combining solar, wind, and biomass with battery storage, microgrids are crucial for providing consistent power to communities not connected to the main grid.
Rooftop Solar: With favorable government policies and incentives, rooftop solar installations have gained momentum. These systems allow individual households and businesses to generate their own power, contributing to energy self-sufficiency and reducing the load on the centralized grid.
Hybrid Solar-Wind Projects: By combining solar and wind energy, hybrid projects can provide more consistent power output. Wind energy tends to be more available during the night and in monsoon seasons, while solar energy is abundant during the day. Integrating these sources allows for more balanced energy generation.
Energy Storage Solutions: Battery energy storage systems (BESS) are becoming an integral part of hybrid systems, enabling the storage of excess renewable energy for use during periods of low generation. This is particularly important for maintaining grid stability and ensuring a reliable power supply.
Biomass-Based Decentralized Systems: Biomass energy, derived from agricultural and forestry waste, is another important component of decentralized energy in rural India. Small-scale biomass plants can generate electricity and heat, providing a sustainable energy solution for rural industries and households.
Policy and Regulatory Support: The Indian government has introduced various policies to promote decentralized renewable energy. Initiatives such as the Pradhan Mantri Kisan Urja Suraksha evam Utthaan Mahabhiyan (PM-KUSUM) scheme encourage the use of solar pumps and decentralized solar power plants for farmers. Additionally, the Electricity Act amendments and draft policies emphasize the importance of decentralization and the integration of renewable energy.
Future Prospects
As India continues to progress toward its renewable energy goals, hybrid energy systems will play a crucial role in achieving energy decentralization. The integration of various renewable sources, coupled with advances in energy storage and smart grid technologies, will create a more resilient and efficient energy system.
In conclusion, hybrid energy systems represent a transformative approach to energy generation in India. By embracing decentralization and integrating multiple renewable sources, India can enhance energy access, improve grid stability, and reduce its carbon footprint. Continued innovation and supportive policies will be key to realizing the full potential of hybrid energy systems in the country's energy landscape.

Developments to increase decentralization in the country >>> Click Here...


Comments
Post a Comment